Go to Slide
Enter slide number (1-36):
💡 Tip: You can also press Ctrl+G to open this dialog
A Hands-On Introduction to Technology
🌐 Internet Basics | 🔧 Hardware | 📧 Email Systems

Welcome to the Hope For Kids Summer Technology Adventure!
🏖️ Did you know we literally taught sand to think? Today you'll discover how a handful of beach sand becomes the brain of your smartphone!
Instructor: Malinda Rathnayake
Quick Icebreaker

🤔 What happens when you type "google.com" and hit Enter?
Our 2-Hour Tech Adventure
🌐 Internet Basics
How devices connect
🔗 DNS & DHCP
The internet's phone book
📧 Email Journey
From send to inbox
🧠 CPU & RAM
How computers think
Plus: Hands-on troubleshooting with real tools! 🛠️
The Internet: A Network of Networks
Your Data Packets Epic Journey 🚀
1. Your Device
You hit "Enter" 💻
Analogy: Writing a letter
2. WiFi Router
Your home's gateway 📡
Analogy: Your mailbox
3. ISP
e.g., Comcast, Verizon 🏢
Analogy: Local Post Office
4. Internet Backbone
Undersea fiber optic cables 🌊
Analogy: Mail trucks & planes
5. Destination Server
e.g., Google's data center ☁️
Analogy: Recipient's Mailbox
From Click to Content in Milliseconds!
This entire journey, crossing thousands of miles, happens faster than you can blink. It's a coordinated dance of hardware and protocols.
🛠️ Let's Try Our First Commands!
Lets Open Your Terminal/Command Prompt
ping google.com
tracert google.comLive Demo Result (ping):
PING google.com (172.217.14.238) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from ord38s34-in-f14.le100.net: icmp_seq=1 time=12.4 ms
64 bytes from ord38s34-in-f14.le100.net: icmp_seq=2 time=11.8 ms
64 bytes from ord38s34-in-f14.le100.net: icmp_seq=3 time=12.1 ms
Live Demo Result (tracert):
Tracing route to google.com [172.217.14.238]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 192.168.1.1
2 5 ms 5 ms 5 ms 10.10.0.1
3 12 ms 11 ms 12 ms 96.120.1.1
4 13 ms 12 ms 13 ms 68.86.90.1
5 15 ms 14 ms 15 ms 209.85.241.100
6 16 ms 15 ms 16 ms 172.217.14.238
Trace complete.
What we're seeing:
- ⏱️ ping: How long it takes to reach Google's servers (milliseconds!)
- 📦 If any data packets get lost along the way
- 🗺️ tracert: The actual path (hops) your data takes through the network to reach its destination
- ping checks if a server is reachable and how fast.
- tracert shows every step (router) your data passes through—great for finding where slowdowns or problems happen!
Quick Understanding Check!
What does the "ping" command actually do?
DNS: The Internet's Phone Book 📞
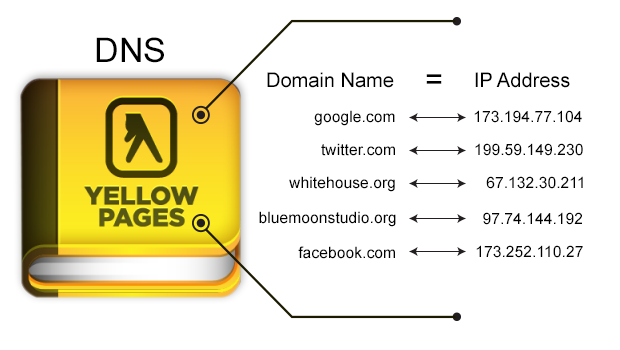
How DNS Works
google.com
(Human-friendly) 😊
172.217.14.238
(Computer address) 🤖
🔍 Let's look up some IP addresses!
We'll use the nslookup command to peek behind the curtain
🛠️ DNS Lookup Demo
nslookup google.comTry these too:
What's that MX command? It finds email servers! We'll use this later for our email journey. 📧
DHCP: The Hotel Front Desk 🏨
New Device
"I need an address!" 🆕
DHCP Server
"Here's 192.168.1.105" 🏷️
Connected!
Ready to browse 🌐
The DHCP Handshake
1. DISCOVER 🔍
"Hello! Anyone have an IP for me?"
2. OFFER 🎁
"Yes! How about 192.168.1.100?"
3. REQUEST 🙏
"Perfect! I'll take it!"
4. ACK ✅
"Confirmed! It's yours for 24 hours!"
🛠️ See Your Network Settings
Look for these important details:
📶 The Wireless Revolution

🏁 WiFi Evolution: What Actually Matters
📻 WiFi 4
50-100 Mbps real-world • 5-10 devices max
🚗 WiFi 5
100-300 Mbps • 15-20 devices, some buffering
🚄 WiFi 6
200-600 Mbps • 30+ devices, smooth streaming
🚀 WiFi 7
400-1200 Mbps • 50+ devices, gaming-ready
Reality Check: Your internet is probably 200-1Gbps anyway. Better WiFi = everyone gets their fair share! 📊
🛠️ Check Your WiFi Generation
Let's discover your WiFi version:
🔍 WiFi Standard Decoder:
- 802.11n = WiFi 4 (Old but still common)
- 802.11ac = WiFi 5 (Pretty good)
- 802.11ax = WiFi 6 (Modern standard) ⭐
- 802.11be = WiFi 7 (Cutting edge) 🚀
🎯 Why WiFi 6/7 Are Actually Game-Changers
📱 OFDMA
Multiple devices share channels efficiently (no more waiting your turn!)
🎯 MU-MIMO
Router talks to 8+ devices simultaneously (family streaming solved)
🔋 Target Wake Time
Smart devices sleep better (phone battery lasts longer)
New WiFi: Organized conversation where everyone gets heard efficiently!
Real benefit: Your Zoom call doesn't lag when someone starts Netflix in the other room! 📹
🚨 Tech Marketing vs Reality Check
📢 Marketing Claims
"WiFi 6: Up to 9.6 Gbps!"
🏠 Real World
Your WiFi 6: 200-400 Mbps
🤔 Why the huge difference?
- Lab conditions: Perfect setup, no interference, one device
- Your home: Walls, microwaves, 20+ devices competing
- Internet bottleneck: Your ISP speed is the real limit
- Distance matters: Speed drops with every wall/floor
🛠️ Let's Test Marketing Claims
Real Speed Test Challenge:
Typical Results:
Critical Thinking: What matters more?
🔌 Ethernet: The Reliable Workhorse
📞 10 Mbps (1980s)
Thick cables, shared bandwidth
🏠 100 Mbps (1990s)
Fast Ethernet, twisted pair cables
🚀 1 Gbps (2000s)
Gigabit - still the home standard
⚡ 10+ Gbps (Now)
Data centers, pro gaming setups
Ethernet: Wired reliability - what you pay for is what you get!
Why gamers still use cables: 1ms latency vs 20-50ms WiFi lag can mean victory or defeat! 🎮
🔌 From Clunky Taps to a Satisfying Click
The Evolution of the Ethernet Plug
🧛 Vampire Tap (1980s)
Drilled into a shared coaxial cable. Bulky and unreliable.

🔄 BNC Connector (90s)
Twist-on for thinner coax. Easier, but one bad cable downed the network.

✅ RJ45 Jack (Today)
The familiar click! Dedicated, reliable, and cheap. The undisputed champ.
☕ 10-Minute Break
Coming up next:
📧 How email travels across the internet using everything we just learned!
We'll trace an email from your click to their inbox using DNS, SMTP, and more!
📧 The Amazing Journey of an Email

🔄 The Complete Email Delivery Process
- 📝 Compose & Send: You hit that send button
- 🔍 DNS Lookup: Server finds recipient's mail server using MX records
- 🤝 SMTP Handshake: Servers establish secure communication
- 📦 Data Transfer: Your message travels securely across the internet
- 📬 Delivery: Email lands safely in recipient's mailbox
- ✅ Acknowledgment: Servers confirm successful delivery
📬 Email Protocols: From Basic to Enterprise
📤 SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Sends emails from your device to the server
Think: Outgoing mail truck
📥 POP3
Post Office Protocol
Downloads emails to your device (then deletes from server)
Think: Taking mail home from P.O. Box
📨 IMAP
Internet Message Access Protocol
Syncs emails across all devices (stays on server)
Think: Shared family mailbox
🏢 MAPI
Messaging Application Programming Interface
Microsoft's protocol for Outlook + Exchange/Office 365
Think: VIP corporate mail service
📱 EAS
Exchange ActiveSync
Mobile-first protocol for Office 365 & Google
Think: Mail that follows you everywhere
📅 CalDAV
Calendar Distributed Authoring and Versioning
Syncs calendars across devices (Google Calendar, iCloud)
Think: Shared family calendar
🏢 What You'll Actually Use in Your Career
- Office 365: MAPI (Outlook desktop) + EAS (mobile apps)
- Google Workspace: IMAP/SMTP + CalDAV + CardDAV
- Personal Email: IMAP + SMTP (Gmail, Yahoo, etc.)
- Mobile Devices: EAS for business, IMAP for personal
🔍 Finding Email Servers (MX Records)
Let's find Gmail's email servers:
Try your school or company domain too!
Those numbers (5, 10, 20) are priorities - lower numbers get tried first! It's like having backup post offices! 📮
🛡️ Email Security: Who Can You Trust?
🆔 SPF
"Are you allowed to send mail for this domain?"
✍️ DKIM
"Is this message tampered with?"
🚨 DMARC
"What should I do if checks fail?"
🧠 CPU: The Computer's Brain

📚 Want to dive deeper?
Learn about transistors, instruction cycles, performance factors, and the future of CPU technology!
⚡ How CPUs Think: Fetch-Decode-Execute
🔍 FETCH
"Get the next instruction from memory"
🧩 DECODE
"What does this instruction mean?"
⚡ EXECUTE
"Do the math or move the data"
💾 STORE
"Save the result"
💾 RAM: Your Computer's Workspace
💽 Storage
Filing cabinet
(permanent but slow) 🐌
💾 RAM
Desk workspace
(temporary but fast) ⚡
🧠 CPU
Your brain
(processes everything) 🤔
📚 Learn More About RAM
Discover memory hierarchy, virtual memory, performance optimization, and troubleshooting tips!
🛠️ Let's Check Your Computer's Performance
Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc)
Click the Performance tab and explore:
- CPU: How hard is your processor working? 💪
- Memory: How much RAM are you using? 🧠
- Processes: What's using your resources? 📊
Experiment: Try opening multiple web browsers and watch the memory usage climb! Then close them and see it drop! 📈📉
🏖️ From Sand to Supercomputers
🏖️ Sand
Silicon dioxide from the beach
🔥 Purify
99.9999999% pure silicon
⚡ Transistors
Billions of tiny switches
🧠 Intelligence
Your smartphone!
Mind-blowing fact: A grain of sand contains about 1 trillion atoms. Modern CPUs have transistors just 50 atoms wide! 🤏
🔬 Want to see the complete process?
🔗 How Semiconductors are Made: Complete Guide
Explore photolithography, clean rooms, transistor formation, and the incredible journey from silicon to supercomputers!
🔧 Mini Troubleshooting Challenge
Scenario: "My internet isn't working!" 😫
Work in pairs - what steps would you take using what we learned?
Your detective toolkit: 🕵️♀️
ping google.com- Test basic connectivityipconfig /all- Check network settingsnslookup google.com- Test DNS resolution- Task Manager - Check system resources
ipconfig /release&/renew- Reset DHCP
🎯 Systematic Troubleshooting
1. Check Physical 🔌
Cables, WiFi, power, lights
2. Test Connectivity 📡
ping 8.8.8.8 (Google's DNS)
3. Check DNS 🔍
nslookup google.com
4. Reset if Needed 🔄
ipconfig /release then /renew
🌟 You Now Understand...
- 🐌 Why websites sometimes load slowly (network hops, DNS delays, server load)
- 📧 How your email knows where to go (MX records, SMTP routing, DNS magic)
- 🔄 Why restarting fixes things (clears RAM, resets connections, fresh start)
- ⚡ What makes computers fast (CPU speed, RAM amount, efficient cooling)
- 🕵️ How to diagnose network problems (ping, nslookup, ipconfig wizardry)
- 🏖️ How we turned sand into thinking machines (silicon purification, transistors)
- 📶 Why WiFi 6/7 is a game-changer (better speeds, more devices, longer battery life)
📚 Keep Learning!
Your Reference Site:
Comprehensive course materials covering everything we learned today and more!
📖 Essential Resources:
- Learning Resources:
🔗 Curated learning platforms, video series, and interactive tools - Technical Glossary:
🔗 Definitions for all technical terms we covered
Practice at home: 🏠
- Try commands on different websites and compare speeds
- Monitor your system performance during different activities
- Look up your school's or company's email servers
- Become the family tech troubleshooter!
- Explore how other devices (smart TV, game console) get their IP addresses
- Check what WiFi version your devices support
📺 Additional Video Resources:
How CPUs Work - Crash Course Computer Science:
🎬 https://youtu.be/FZGugFqdr60
Deep dive into CPU architecture and how computers process information
🤔 Questions & Discussion
Reflect on:
- 💡 What you want to explore further
- 📱 How this applies to your daily tech use
- 🔮 What other technology mysteries you'd like solved
- 🚀 Whether you're more interested in networking, hardware, or programming
- 📶 How WiFi 6/7 might change your home setup